Which of the Following Is a Type of Lipid
Usually due to some large hydrocarbon chain. Has 2 non-polar hydrophobic tails.
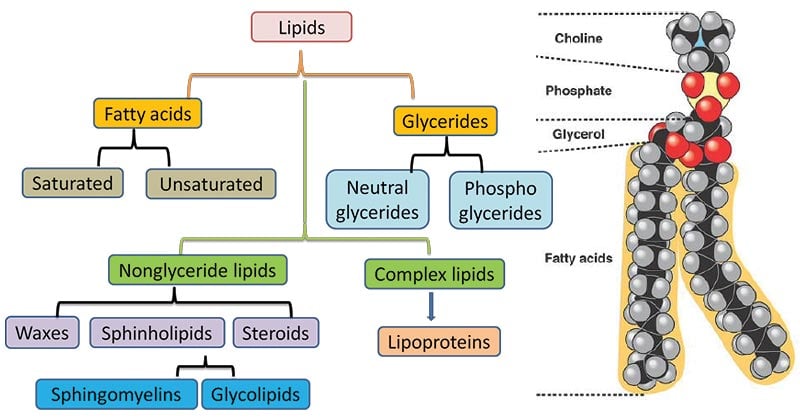
Lipids Definition Properties Structure Types Examples Functions
The type of lipid that gives a cell membrane its shape is a A triacylglycerol.

. This module explores the world of lipids a class of compounds produced by both plants and animals. Click here to get an answer to your question Which of the following is a type of lipid. A phosphatidylinositol b cerebroside c ganglioside d globoside 19_____ Which would be a property of all the major types of lipids in this membrane.
________________ is a membrane lipid composed of sphingosine fatty acid and a simple sugar. An example of a saturated fat is a olive oil. Neutral or True Fats.
There are three main types of lipids. Which of the following is a type of lipid. Lipid can have polar hydroxyl groups but only as part of a molecule with overall non-polar character usually due to some large hydrocarbon chain.
On this page well learn about the structures of these three types of lipids as well as their functions in the body and where you can find them in foods. Lipids play a number of key roles in the body including protecting cells and allowing for the. Which of the following is not a type of post translational modification.
Which of the following are lipids. Match the following definitions to the terms they describe. Clinical remission partial remission partia.
Triglycerides are the main form of lipids in the body and in foods. Glycerol has a polar hydroxyl group for every carbon atom and. 18_____ Which type of membrane lipid contains an acidic oligosaccharide.
Triglycerides phospholipids and sterols. Fats oils waxes steroids certain plant pigments and parts of the cell membrane these are all lipids. A Triacylglycerols B Glycerophospholipids C Sphingolipids D Gangliosides E none of the above Ans.
Which of the following lipid types is the least polar. Serve as food reserves in many organisms. WINDOWPANE is the live-streaming social network and multi-media app for recording and sharing your amazing life.
CELL MEMBRANE-A phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that forms the boundary of all cells PHOSPHOLIPID- A. A Level of Difficulty. A complex amino alcohol backbone for membrane lipids.
It begins with a look at the chemical reaction that produces soap and then examines the chemical composition of a wide variety of lipid types. Medline EMBASE and Ovid were searched using the following search terms. Which of the following is a type of lipid.
Makes up the cell membrane. A literature search was conducted to identify publications addressing the early phases of lipid phenotypes in children and adults with either type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes. More than 95 percent of lipids in the diet are in the form of triglycerides.
Has a polar hydrophilic head. Usually due to some large hydrocarbon chain. Step by step answerIn biology and biochemistry the lipid is a macro biomolecule that is soluble in non-polar solventsNonpolar solvents are typically hydrocarbons used to dissolve all other naturally occurring hydrocarbons.
Which of the following is NOT a type of lipid. Its when the amounts are outside of normal ranges that these lipids may cause serious health issues. Post comments photos and videos or broadcast a live stream to friends family followers or everyone.
C include fats that consist of one fatry acid molecule and three glycerol. Lipid can have polar hydroxyl groups but only as part of a molecule with overall non-polar character. The main types of lipids include sterols like cholesterol and triglycerides.
Triglycerides c oils d waxes e all of the above 35. Include cartilage and chitin. CELL- basic structural unit of living organisms.
Neutral or True Fats 2. A They would be saponifiable in base and hydrolyzed in acid. The common name of hexadecanoic acid is.
Both of these types are essential to the body at healthy levels. The following points highlight the ten important types of lipids. Which specific lipid has the following characteristics.

This Photo Displays The Different Lipoproteins And Where They Transport Lipid To From Anabolic Biochemistry Nutrition

Chapter 13 Lipids Chemistry 20 Lipids Family Of Bimolecules They Are Soluble In Organic Solvents But Not In W Cell Membrane Membrane Structure Solubility

Comments
Post a Comment